gradle task示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 task compile << { println "Compiled" } task clean << { println "Clean" }
task之间相互依赖
compile.dependsOn clean
执行顺序 1 compile.mustRunAfter clean
自定义Property 1 2 3 4 ext.property1 = "this is property1" ext{ property2 = "this is property2" }
依赖其他moudle 1 2 3 dependencies { compile project (':library' ) }
Gradle为每个moudle都会生成一个build.gradle,为了管理这些moudle,他还会在根目录下生成一个build.gradle
allprojects()方法将repositories配置一次性地应用于所有的module(子Project)和root-project本身,当然也包括定义的Task,这个task配置到所有module里面了和root-project。
###引入其他的Gradle文件的task1 apply from : '../nuild-config/build.gradle'
控制输出名称和路径 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 android.applicationVariants.all { variant -> variant.outputs.each { output -> def outputFile = output.outputFile if (outputFile != null && outputFile.name.endsWith('.apk' )) { def fileName = outputFile.name; if (android.defaultConfig.versionName != null ) { fileName = fileName.replace(".apk" , "-${android.defaultConfig.versionName}.apk" ) } if (project .hasProperty('OUT_PUT_APK_SUFFIX_PARA' )) { fileName = fileName.replace(".apk" , "-${OUT_PUT_APK_SUFFIX_PARA}.apk" ) } def today = new Date().format('yyMMddHHmm' ); fileName = fileName.replace(".apk" , "-${today}.apk" ) if (project .hasProperty('OUT_PUT_DIR_PARA' )) { File output_dir1 = file ("${OUT_PUT_DIR_PARA}" ); output.outputFile = new File (output_dir1, fileName) println "输出文件位置: " + output.outputFile } else { output.outputFile = new File (outputFile.parent, fileName) println "输出文件位置: " + output.outputFile } } } }
###拼接字符串1 2 ext.tem = 'tem' def name = "my name is $tem"
Gradle执行顺序 dependsOn 如果我们想执行的task A依赖于task B
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 task A << { println "Hello From A" } task B << { println "Hello From B" } A.dependsOn B
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 task A << {println 'Hello from A' }task B { dependsOn A doLast { println 'Hello from B' } }
这样我们执行Gradle B的时候就会先执行 A,上面两种写法的效果是一样的。
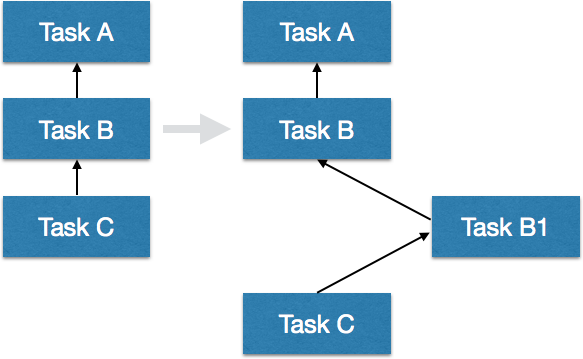
如果我们想在已近存在task依赖中插入我们的task,改怎么办呢?
1 2 3 4 5 task A << {println 'Hello from A' }task B << {println 'Hello from B' }task C << {println 'Hello from C' }B.dependsOn A C.dependsOn B
加入我们的新task
1 2 3 task B1 << {println 'Hello from B1' }B1.dependsOn B C.dependsOn B1
执行Gradle c
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 paveldudka$ gradle C :A Hello from A :B Hello from B :B1 Hello from B1 :C Hello from C
###mustRunAfter
1 2 3 4 5 6 task unit << {println 'Hello from unit tests' }task ui << {println 'Hello from UI tests' }task tests << {println 'Hello from all tests!' }tests.dependsOn unit tests.dependsOn ui
执行Gradle tests结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 paveldudka$ gradle tests :ui Hello from UI tests :unit Hello from unit tests :tests Hello from all tests!
尽管unit和UI会在tests之前执行,但是UI和unit的执行顺序是不能保证的,虽然看起来是按照字母表的执行,但这依赖于Gradle的默认实现,我们也不清楚具体是怎样的规则,因此如果们有先后顺序的区分,我们就不能依赖这种顺序
如果我希望unit先执行,然后子啊执行UI,一个解决办法就是UI依赖unit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 task unit << {println 'Hello from unit tests' }task ui << {println 'Hello from UI tests' }task tests << {println 'Hello from all tests!' }tests.dependsOn unit tests.dependsOn ui ui.dependsOn unit
但是有个问题,我们的UI task并不依赖于 unit ,每次执行UI task的时候都会执行unit,这就要用到 mustRunAfter了。这里指定 ui.mustRunAfter unit,这样如果UI和unit同事存在的时候,Gradle会先执行unit,他们也可以单独执行
###finalizedBy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 task unit << {println 'Hello from unit tests' }task ui << {println 'Hello from UI tests' }task tests << {println 'Hello from all tests!' }task mergeReports << {println 'Merging test reports' }tests.dependsOn unit tests.dependsOn ui ui.mustRunAfter unit mergeReports.dependsOn tests
这个task是能工作,但是看起来好笨啊。mergeReports从用户的角度来看感觉不是特别好。我希望执行tests task就可以获得测试报告,而不必知道mergeReports的存在。当然我可以把merge的逻辑挪到tests task中,但我不想把tests task搞的太臃肿,我还是继续把merge的逻辑放在mergeReports task中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 task unit << {println 'Hello from unit tests' }task ui << {println 'Hello from UI tests' }task tests << {println 'Hello from all tests!' }task mergeReports << {println 'Merging test reports' }tests.dependsOn unit tests.dependsOn ui ui.mustRunAfter unit mergeReports.dependsOn tests tests.finalizedBy mergeReports
现在执行tests task就可以拿到测试报告了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 paveldudka$ gradle tests :unit Hello from unit tests :ui Hello from UI tests :tests Hello from all tests! :mergeReports Merging test reports
donate
感谢鼓励